Breaking Down the Different Types of Health Insurance
By comprehending its fundamental principles, selecting a health plan can become a simpler process.
Understanding health insurance may appear daunting due to its intricate nature. However, by comprehending its fundamental principles, recognizing the variety of plan options, and considering individual health requirements, selecting a plan can become a simpler process. Additional knowledge about the availability of several government-backed programs significantly impacts the decision-making process in choosing the most suitable insurance policy. Despite its complexities, this valuable information serves as a crucial resource for making informed healthcare decisions.
Understanding the Basics of Health Insurance
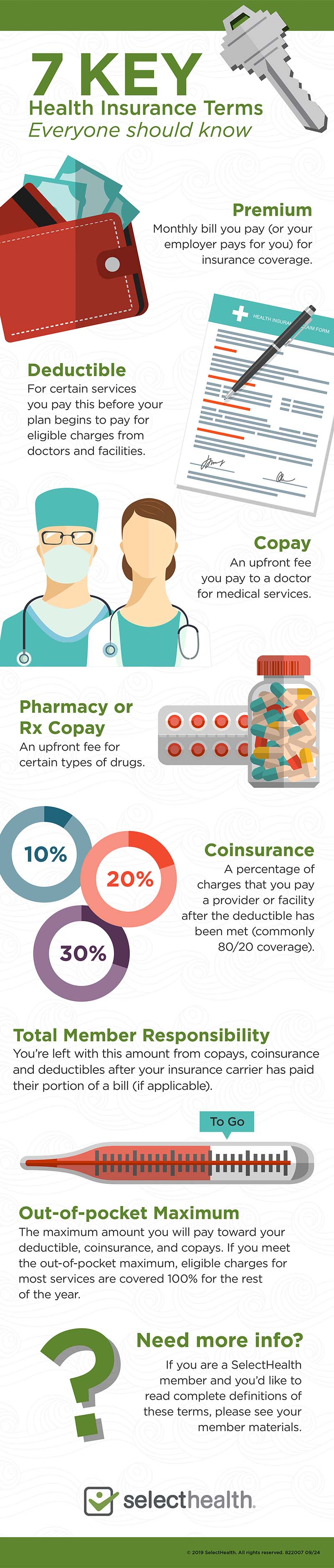
For individual plans, consider health insurance as an agreement between an individual and an insurance provider. A set amount is paid periodically, referred to as a premium, and in return, the insurance provider offers assistance with healthcare costs. It's important to understand several key terms when studying coverage options.
To start with, there's the term 'deductible', which essentially represents the initial cost that needs covering before the insurance provider starts contributing. Following this, copayment comes into play; a set sum that's required for certain healthcare services. Of utmost importance is understanding the out-of-pocket maximum. This refers to the limit on the total amount an individual will have to pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services in a single year.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Diving into healthcare often feels like you're swimming in an alphabet soup of acronyms. Terms like Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs), Point of Service (POS) plans, High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs), and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tossed around frequently. Once the layers are peeled back, these are all just different types of health insurance plans, each uniquely tailored to cover specific needs.
HMOs
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) require members to choose a primary care physician. You should also contact your insurance provider to find out if you need a referral. A key feature of HMOs is typically lower out-of-pocket expenses. However, these plans often lack flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Lower cost and a preventive approach to healthcare are two primary advantages. Limited healthcare provider choice and required referrals can be viewed as disadvantages. Summing it up, HMOs provide cost advantages and focus on preventive care, but come with certain restrictions and referral necessities.
PPOs
In essence, Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) are health insurance plans that provide the freedom to choose doctors or specialists without referrals. Understanding the balance between benefits and costs is crucial, as higher out-of-pocket expenses often accompany this independence. PPOs present an expanded range of choices for healthcare providers and hospitals. However, it's this very flexibility that may lead to higher expenses. The benefits of increased flexibility and eliminated need for referrals stand out. One crucial point to note is the potential for higher costs which could sneak up unexpectedly, coupled with a limited focus on preventative care. A careful evaluation of advantages and disadvantages is necessary to determine whether a PPO suits individual needs.
EPOs
An Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) is a unique health insurance plan that combines features of a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) and a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO). It provides flexibility like a PPO and cost containment like an HMO. With an EPO, there's usually a specified network of providers. To benefit from the coverage, staying within this network is required. One benefit, however, is the lack of necessity for referrals when seeking specialists. EPOs are often cheaper and more flexible than HMOs, making them appealing. But, they may provide less flexibility than PPOs and require strict adherence to a specific network to receive coverage benefits.
POS Plans
A Point of Service (POS) plan marries the characteristics of both Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) in the context of health insurance. This unique mechanism typically requires the selection of a primary care physician along with obtaining referrals to specialist services.
However, it does grant the flexibility of consulting clinicians outside the network, although at an extra charge. In comparison to a PPO, a POS plan proves more economical and offers greater adaptability than an HMO. But bear in mind, confirming the necessity of obtaining referrals is something you should discuss with your insurance provider, being that healthcare services from providers outside the network can rack up higher expenses.
HDHPs with HSAs
Think of a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) like a health insurance plan with a twist: it offers the benefit of lower monthly premiums, yet sets the bar a little higher in terms of deductibles. There's also something known as a Health Savings Account (HSA). This isn't just a way to save for health-related costs—it's a method that comes with tax benefits. When pairing an HDHP with an HSA, it can be a smart financial move. The policyholder can enjoy lower premiums every month and also have a tax-free account for those inevitable health expenses. But remember, there's a trade-off—the deductible will be higher, and there may be a need to pay out a bit more from personal reserves in order to cover the cost.
Choosing the Right Plan
When choosing health insurance, it's important to balance health needs, budget, and preferences for certain medical providers. Looking at summaries of benefits and coverage limits will reveal what is covered and what financial responsibilities remain for the insured. Reviewing the included provider network, prescription drug coverage, and any extra benefits, can be helpful. Remember, every question matters when it involves health. Consequently, all inquiries should be brought to a knowledgeable insurance expert without delay.
Government-Sponsored Health Insurance Programs
In addition to an array of private health insurance plans, the government provides a handful of programs to those who fulfill specific criteria. These include programs like Medicare, Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, known as CHIP. For a significant number of individuals, these government-sponsored health insurance options can literally be a saving grace.
Medicare
As a comprehensive federal health insurance program, Medicare reaches beyond the scope of serving solely seniors over 65. In fact, it stretches its support to include younger policyholders who face certain disabilities and individuals tackling the trials of End-Stage Renal Disease (a permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant). Yet, it's important to recognize that Medicare does not adopt a one-size-fits-all approach. Instead, it's designed with multiple sections, each covering different services. Consequently, an enrollee might find hospital insurance, medical insurance, and prescription drug coverage all included within this program.
Medicaid
Medicaid has deep roots in the health insurance field. It's an incredibly important aid program, fueled by both federal and state funding. Designed with the disadvantaged at heart, it aims to alleviate medical expenses for those with limited income and scarce resources. The interesting part is it provides benefits beyond what Medicare typically covers. It includes coverage for nursing home care and personal care services. Although, keep in mind, eligibility for Medicaid is dependent on income level and other factors, and these criteria can vary from state to state.
Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
CHIP provides low-cost health coverage to children in families that earn too much money to qualify for Medicaid. In some states, CHIP also covers pregnant women. Each state offers CHIP coverage and works closely with its state Medicaid program.
Additional Considerations
When it comes to health insurance, there's no single solution that fits everyone's needs - it's a much more expansive field. This includes distinctive alternatives such as short-term health insurance plans and supplemental insurance. The latter can provide coverage for vision, dental, and accident insurance. The introduction of the Affordable Care Act has also contributed to a significant shift, changing the landscape, and thus broadening the range of health insurance options available for consideration.
Feeling puzzled by health insurance? It's not as intimidating as it first appears. With the right information, choosing an appropriate plan becomes straightforward. Before diving in, take the time to evaluate specific needs. This step ensures that the chosen plan provides sufficient coverage. Remember, assistance is available whenever it's needed. Information and guidance are just a click away with Select Health.